Informal Design Guidelines for Relation Schemas
ในบทความนี้จะกล่าวถึง Guidelines ของการออกแบบ Relation Schemas ซึ่งมีอยู่ 4 Guidelines ซึ่งจะทำให้ Database นั้นดียิ่งขึ้น
Informal Design Guidelines
for Relation Schemas
- Measures of quality
- Making sure attribute semantics are clear: ให้แน่ใจว่า ความหมายของแต่ละ attribute มีความชัดเจน
- Reducing redundant information in tuples: ลดความ ซําซ้อนของข้อมลูใน tuples
- Reducing NULL values in tuples
- Disallowing possibility of generating spurious
(false) tuples: ไม่อนุญาตให้เกิด spurious tuples คือ tuples
ที่ผิดพลาด เช่น ได้ข้อมูลเกินจากความเป็นจริงหลังจากรวมข้อมูลจากหลาย
Table หรือ Relation
Imparting Clear Semantics to
Attributes in Relations
- Semantics of a relation
- Meaning resulting from interpretation of attribute values in a tuple: ความหมายที่สะท้อนถึง relation มาจากการแปลความหมายของค่า
ข้อมูล attribute ต่างๆที่อยู่ใน tuple
- Easier to explain semantics of relation
- Indicates better schema design: จะต้องอธิบายความหมายของ relation แต่ละ relation ได้ง่าย
Guideline 1
- Design relation schema so that it is easy to explain its meaning: ต้องออกแบบให้สามารถอธิบายความหมายของ relation แต่ละ relation ได้ง่าย
- Do not combine attributes from multiple entity types and relationship types into a single relation: ต้องไม่รวม attribute ที่มาจากหลาย domain ไว้ใน relation เดียว
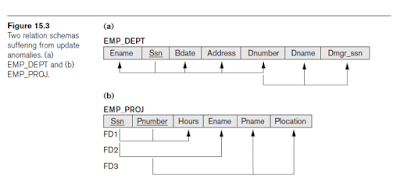
Redundant Information in Tuples and Update Anomalies
- Grouping attributes into relation schemas
- Storing natural joins of base relations leads to update anomalies: การจัดเก็บข้อมูลที่อยู่ต่าง domain ถึงแม้จะมีความสัมพันธ์กันในลักษณะ natural joins ก็สามารถนําไปสู่ปัญหา update anomalies ได้ (ปัญหาการปรับปรุงข้อมูลที่ทําให้ข้อมูลมีลักษณะผิดปกติ)
- Types of update anomalies:
- Deletion
- Modification
Guideline 2
- Design base relation schemas so that no update anomalies are present in the relations: ต้องออกแบบไม่ให้เกิด update anomalies ในแต่ละ relation
- If any anomalies are present: ถ้าหลีกเลี่ยงไม่ได้
- Make sure that the programs that update the
database will operate correctly: ให้แน่ใจว่าโปรแกรมจะ
ปรับปรุงข้อมูลในฐานข้อมูลได้ถูกต้อง
NULL Values in Tuples
- May group many attributes together into a “fat” relation
- Problems with NULLs: ปัญหาการจัดเก็บค่า NULL ทําให้ เกิด
- Problems understanding meaning: การเก็บข้อมูลที่เป็นค่า
NULL อาจจะส่งผลในแง่ไม่สื่อความหมาย หรือเข้าใจความหมายได้ยาก
Guideline 3
- Avoid placing attributes in a base relation whose values may frequently be NULL หลีกเลี่ยงการจัดเก็บ attribute ที่มีโอกาสจัดเก็บค่า NULL จํานวนมากๆ
- If NULLs are unavoidable: แต่ถ้าหลีกเลี่ยงไม่ได้
Generation of Spurious Tuples
- NATURAL JOIN
- Result produces many more tuples than the
original set of tuples in EMP_PROJ
- Called spurious tuples
การรวมข้อมูล (relation) ที่มีความสัมพันธ์กัน แต่เลือก attribute ที"เป็ น
ตัวเชื่อมความสัมพันธ์ไม่เหมาะสม จะทําให้เกิด spurious tuples
- Represent spurious information that is not valid:
การที่มีข้อมูล spurious เกิดขึ้นนั้นหมายความว่า ออกแบบไม่ถูกต้อง
Guideline 4
- Design relation schemas to be joined with equality conditions on attributes that are appropriately related
- Avoid relations that contain matching attributes that are not (foreign key, primary key) combinations ให้หลีกเลี่ยงการนํา attribute ที่ไม่ใช่ foreign key หรือ primary key มาเป็น ตัวเชื่อมโยง ระหว่าง 2 relation
Reference
Fundamentals of Database Systems Sixth Edition : Ramez Elmasri, Shamkant B. Navathe
http://www.cs.science.cmu.ac.th/course/204222/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=ch15_fd_normalization.pdf





ไม่มีความคิดเห็น:
แสดงความคิดเห็น